The Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics (PCBS)
Announces the Main Results of the Palestinian Multiple Indicators Cluster Survey (PMICS) 2019-2020
Ramallah – 15 December 2020 - The Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics, in cooperation with UNICEF, today announced the main results of the Palestinian Multiple Indicator Cluster Survey (MICS) 2019-2020. This announcement was made at a virtual conference with H.E. Dr. Ola Awad, President of PCBS, and Ms. Lucia Elmi, Special Representative of UNICEF in the State of Palestine, and in the presence of representatives of ministries, officials and civil institutions, universities, research centers, United Nations organizations, relevant bodies and the media.
Opening the conference, H.E. Dr. Ola Awad outlined PCBS’s implementation of the PMICS in its sixth round in December 2019 - January 2020. The MICS was implemented with technical and financial support from UNICEF, the French Development Agency (AFD), and the French Ministry of Foreign Affairs, and UNFPA through a survey sample of 10,080 households.
Dr. Awad stated that the main objectives of this survey were to provide updated data necessary to assess the situation of children and women, contribute to increasing awareness of issues related to household and reproductive health. It also provided the data necessary to evaluate the progress made towards achieving the SDG 2030 and other internationally agreed goals. In addition, the MICS has made data available to decision-makers and policy-makers to monitor, develop or modify services. The survey also supports the identification of necessary interventions, and contributes to improving data monitoring systems in Palestine, and enhancing technical expertise in designing and implementing systems.
Ms. Lucia Elmi highlighted that the MICS survey is an international program for conducting household surveys, prepared and developed by UNICEF. Its purpose is to collect statistics on the main indicators used in assessing the children’s and women’s rights, including on the health, nutrition, education and protection status of children, as well as maternal health and household conditions. The survey included five questionnaires: a household questionnaire, a questionnaire for women aged 15-49 years, a questionnaire for children from the ages of 5-17 years old, a questionnaire for children under five years of age, and a questionnaire for testing water quality.
The Main Findings of the Palestinian Multiple Indicators Cluster Survey (PMICS) 2019-2020 are as follows:
Early childhood mortality
The mortality rate among children under-five years in Palestine was 14 per 1000 live births; 15 in the West Bank and 14 in the Gaza Strip. On the other hand, infant mortality rates in Palestine reached 12 per 1000 live births; 12 in the West Bank and 13 in the Gaza Strip. Data also indicated a decline in the child mortality rate during the past ten years, where this percentage reached 15 childern per 1000 live births.
Total Fertility Rates
Total fertility rates in Palestine reached 3.8 births per woman; 3.8 births in the West Bank and 3.9 births in the Gaza Strip.
The adolescent fertility rate (age 15-19 years) in Palestine was 43 births per 1000 women. This rate was higher in the Gaza Strip with 48 births per 1000 women compared to 39 births per 1000 women in the West Bank. When comparing the results with the data of the Palestinian Multiple Cluster Survey 2014, the total fertility rate among women in the age group of 15-49 years old in Palestine reached 4.1 births per woman. Also, the adolescent fertility rate in the age group 15 – 19 years reached 48 births per 1000 women in 2014.
Prevalence of family planning methods
More than half of married women aged 15-49 years in Palestine are currently using a family planning method, or their husband is using one (57.3%); about 56% in the West Bank and about 59% in the Gaza Strip. Data also indicated that about 43% of women use modern methods, whereas about 15% use traditional methods. It is worth mentioning that the percentage of women at the age group 15-49 years old who used family planning methods reached about 57% according to the data of 2014.
61% of married women in the age group of 15-49 years had met their need for modern family planning methods; about 62% in the West Bank and about 60% in the Gaza Strip.
Reproductive Health among women in the age group of (15-49) years
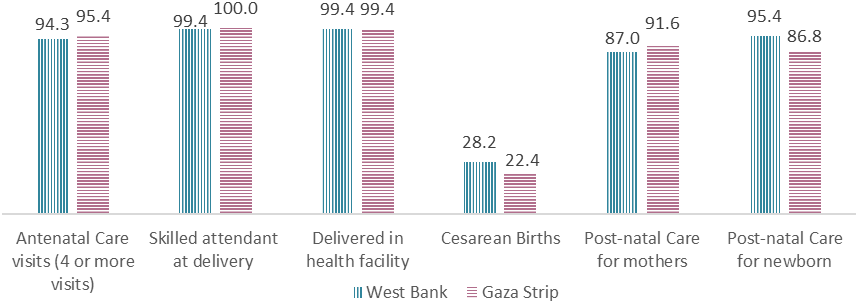
About 95% of women aged 15-49 years received antenatal health care at least four times by a health care provider during pregnancy; and about 73% of women in the same age received health care eight times or more during pregnancy. This percentage reached about 96% in 2014 among women aged 15-49 years who received health care during pregnancy at least four times.
Most births in Palestine occur in health institutions, where about 99% of births took place. Of all live births about 100% were attended by skilled health staff. Data also indicated that about 26% of births underwent Caesarean section. This percentage is no different from the percentage in 2014, as the percentage of births carried out in health institutions reached about 99%, whereas the percentage of births carried out under the supervision of qualified medical staff reached about 100%.
Some 89% of women 15-49 years received health care after birth (postnatal care) during their stay in the health institutions. Data also showed that about 92% of newborns received health care, either while in the health facility, at home after birth, or received health care within two days after childbirth.
Continuum of Reproductive and Maternal and new-born health Interventions by Region
|
|
Safe Water Sources
Some 99% of household members in Palestine use basic drinking water services[1], where this percentage was about 100% in the West Bank compared to about 99% in the Gaza Strip. On the other hand, the percentage of household members who use safely managed water sources[2] was about 40% in Palestine, with a marked difference between the West Bank and the Gaza Strip. The percentage was about 66% of household members who use safely managed water sources in the West Bank, and about 4% of households use safely managed water sources in the Gaza Strip.
Use of Sanitation
Some 98% of household members in Palestine use improved sanitation facilities that are not shared with other households. This percentage reached about 98% in the West Bank while it reached about 97% in the Gaza Strip.
Hand Washing
The percentage of household members who have a hand-washing facility that contains water and soap was about 95%; with about 96% in the West Bank and 95% in the Gaza Strip.
Malnutrition among Children Under Five Years
Stunting prevalence: 8.7% of children under the age of five years in Palestine suffer from moderate and severe stunting. The percentage was 8.5% in the West Bank and 9.0% in the Gaza Strip. When comparing the results with data of 2014, the 2019 percentage has increased, as it was 7.4% in 2014.
Underweight prevalence: 2.1% of children under the age of five years in Palestine suffer from being underweight. This percentage was equal in both the West Bank and the Gaza Strip (2.1%). Available data indicates an increase in the percentage of children under five years who suffer from being underweight, where it reached 1.4% in 2014.
Wasting prevalence: 1.3% of children under the age of five years in Palestine suffer from wasting. The percentage was 1.7% in the West Bank and 0.8% in the Gaza Strip. This percentage has remained steady as compared to 2014, when it reached 1.2%.
The percentage of children under five years by nutritional status and sex
|
Female |
Male |
Malnutrition Indicators |
|
8.8 |
8.6 |
Stunting |
|
1.6 |
2.6 |
Underweight |
|
1.3 |
1.3 |
Wasting |
Functional Capabilities of Children
Some 2% of children in the age group 2-4 years have at least one disability, with a higher rate in the Gaza Strip as compared to the West Bank, reaching about 3% and 2%, respectively. The disability rate was about 15% among children aged 5-17 years; about 17% in the West Bank compared to about 13% in the Gaza Strip.
Early Childhood Development Index
The child development index reached about 84% for children aged 3-4 years who follow the correct development path in at least three of the following four areas: literacy and numeracy (38%); physical development (99%); social-emotional development (82%); and learning (93%).
The data shows that children’s early childhood development has improved from the rate of 72% in 2014.
Child Discipline
Some 90% of children aged 1-14 years were subjected to at least one form of psychological or physical punishment by household members during the month preceding the day of the interview; about 88% in the West Bank compared to about 92% in the Gaza Strip. There were about 92% of male and 88% of female children subjected to psychological or physical punishment during the month preceding the day of the interview in the same age group.
Early Marriage
Results indicate that about 13% of women aged 20-24 years got married for the first time before reaching the age of 18 years; about 11% in the West Bank compared to about 17% in the Gaza Strip.
This percentage has decreased compared to 2014, when the percentage of women aged 20-24 years who were married for the first time before turning 18 years of age reached about 24%.
Exposure to abuse
The percentage of women aged 15-49 years who experienced physical violence, robbery or assault in the last year was about 4%. The percentage by region was about 1% in the West Bank and about 7% in the Gaza Strip.
[1] Basic drinking water services refer to an improved source, provided collection time is not more than 30 minutes for a roundtrip including queuing. Improved drinking water sources are those that have the potential to deliver safe water by nature of their design and construction.
[2] Safely managed water sources means: Improved drinking water source located on premises, free of E. coli and available when needed.